![]() Ultrasound
/ Interventional
Radiology
Ultrasound
/ Interventional
Radiology
![]() i
Current
pathology imaging
guidelines
i
Current
pathology imaging
guidelines
@
Swiss
Physicians
email directory
Digital Roentgenology

example of X-ray and digital fluoroscopy inclinable table
- Conventional radiological procedures listed hereafter all use roentnograms obtained with an X-ray tube:
- Chest, bone and soft tissues roentnograms
- Mammography - galactography - stereotaxy
- Fluoroscopy (real time X-ray study of the body)
- Sialography (salivary gland canals opacification)
- Cholecystography (gallbladder opacification)
- Barium meal (upper digestive tract study by ingestion of a barium suspension)
- Small bowel enema (small intestine study)
- Barium enema (colonic study)
- Intravenous pyelography (excretory urography for kidney diseases)
- Phlebography (vein study)
- Fistulography (fistula tract opacification)
- Arthrography (joint space opacification)
- Hysterosalpingography (uterus and fallopian tube opacification)
- Radiculography (lumbar nerve roots study)
- Angiography with digital substraction (artery or vein opacification)
X-rays are a form of radiant energy, like light, radio or TV waves but they have a shorter wave length, as can be seen hereafter, enabling them to go through matter

Radioprotection: diagnostic medical radiation exposure is anavoidable but it usually represents only a small part of environmental natural radiation exposure, as shown in table hereafter. According to strict radioprotection laws, every effort is made to minimize patient dose without compromizing diagnostic efficiency
|
Diagnostic procedure |
|
|
|
|
X-ray examinations:
Radionuclide studies:
|
|
|
|
See also Radiation Dose Calculator, UIC - Radiation and Life
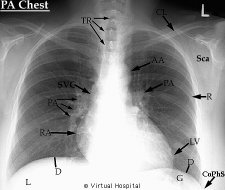
Example of X-ray film: chest